ETRI Ushers in an Era of Realistic Remote Collaboration
Vol.84 August
- Reproducing Facial Expressions, Eye Contact, and Handshakes...Realistic Remote Collaboration Technology Unveiled
- ‘Joining’ Virtual Participants in Actual Conference Rooms...Realizing the Future Collaboration Environments
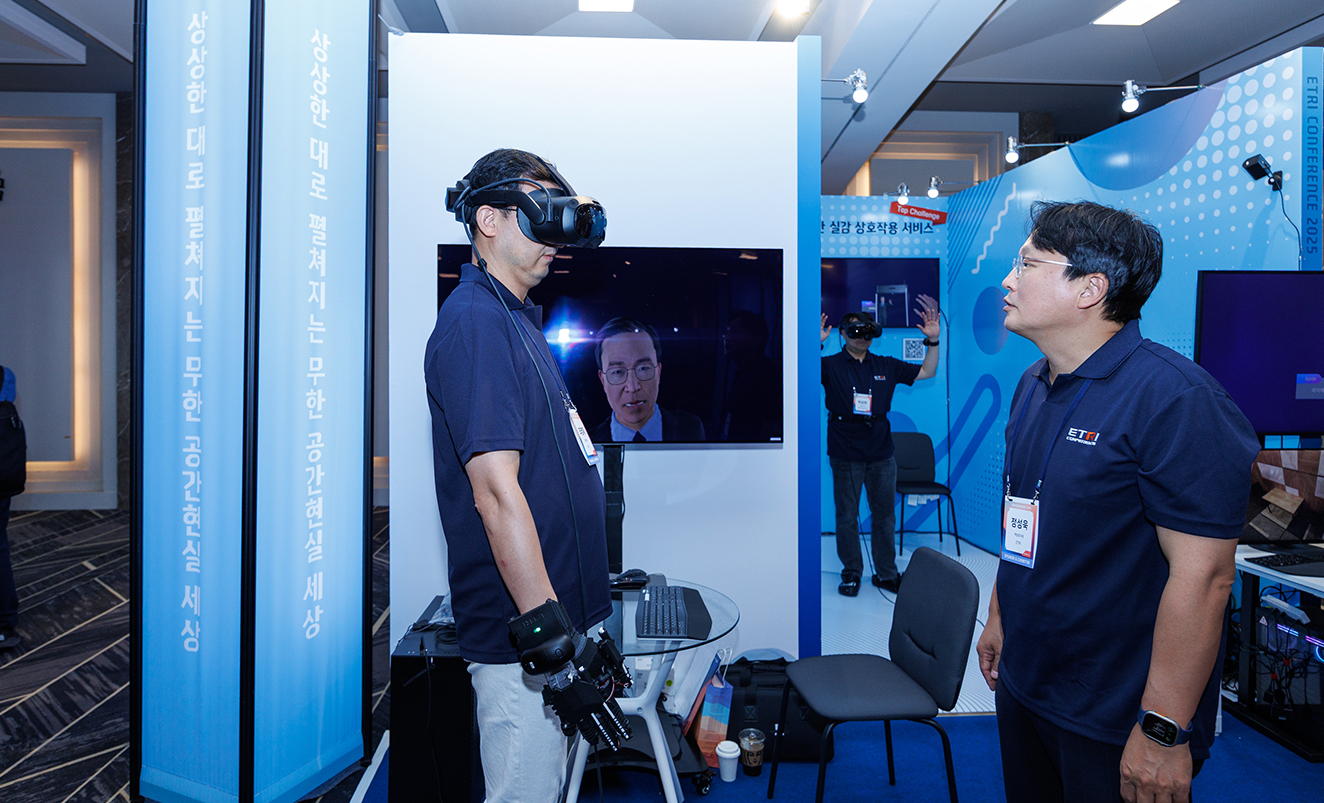

Korean researchers have unveiled next-generation remote collaboration technology that enables users to meet face-to-face and even shake hands in real time with their counterparts as if they were in the same room. Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that it has publicly introduced for the first time “telepresence augmentation technology for eXtended Reality (XR)1) environments” which can precisely reproduce facial expressions, gazes, and even handshakes.
1) eXtended Reality (XR): It is a technology that fuses the real and virtual worlds to create new experiences for users, and is an upper concept that includes virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality.
 Virtual handshake
Virtual handshake
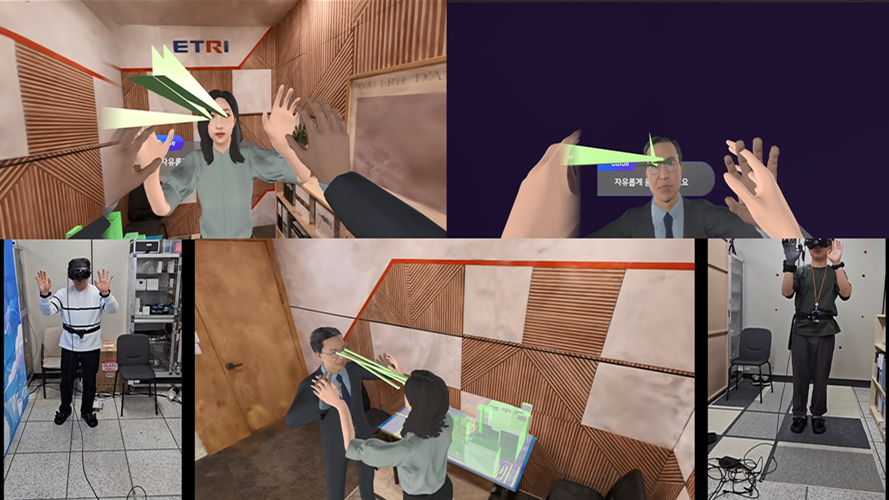 Virtual high five
Virtual high five
The new technology allows two users in different physical locations to simultaneously participate in a meeting within Virtual Reality (VR)2) and Augmented Reality (AR)3) environments, enabling immersive interaction as if they were sitting face-to-face in a real meeting room. This is a next-generation technology that bridges real and virtual spaces. Visitors were able to vividly experience a new form of collaboration by making eye contact and shaking hands with remote participants on-site.
The remote presence augmentation technology developed by ETRI consists of two core components: exoskeleton-based active virtual handshake technology and real-time digital human stereoscopic immersion technology.
2) Augmented Reality (AR): A technique for superimposing a three-dimensional virtual image on an actual spatial image.
3) Virtual Reality (VR): A technique for superimposing three-dimensional virtual images in virtual space.
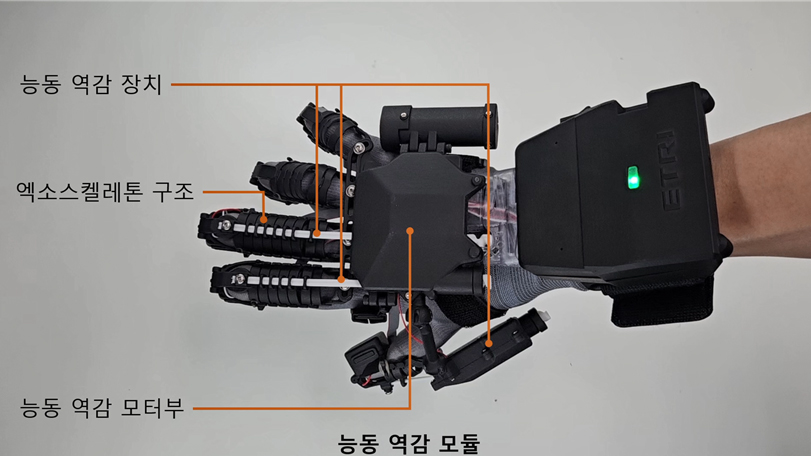 Active force feedback module in the exoskeleton-type Active Type XR haptic glove
Active force feedback module in the exoskeleton-type Active Type XR haptic glove
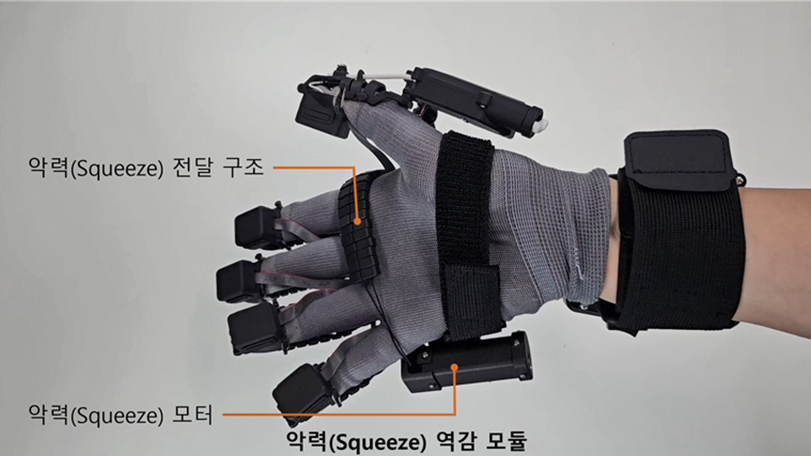 Squeeze force feedback module in the exoskeleton-type Active Type XR haptic glove
Squeeze force feedback module in the exoskeleton-type Active Type XR haptic glove
First, the exoskeleton-based active virtual handshake technology is an advanced tactile feedback skill designed to let users feel not only the movement of their hands, but also the strength and direction of the other person’s grip in real time. To accomplish this, the researchers independently designed and developed an exoskeleton-type Active Type XR haptic glove. These haptic gloves go beyond simple vibrations to deliver a precise tactile experience that closely mimics a real handshake. This allows users to feel the other person’s hand squeeze in real time, creating an immersive interaction that feels like holding hands, even in remote environments.
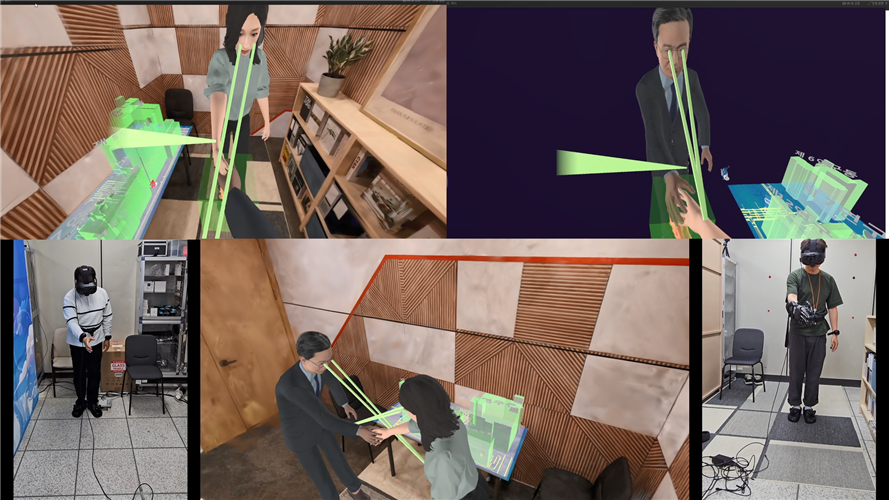
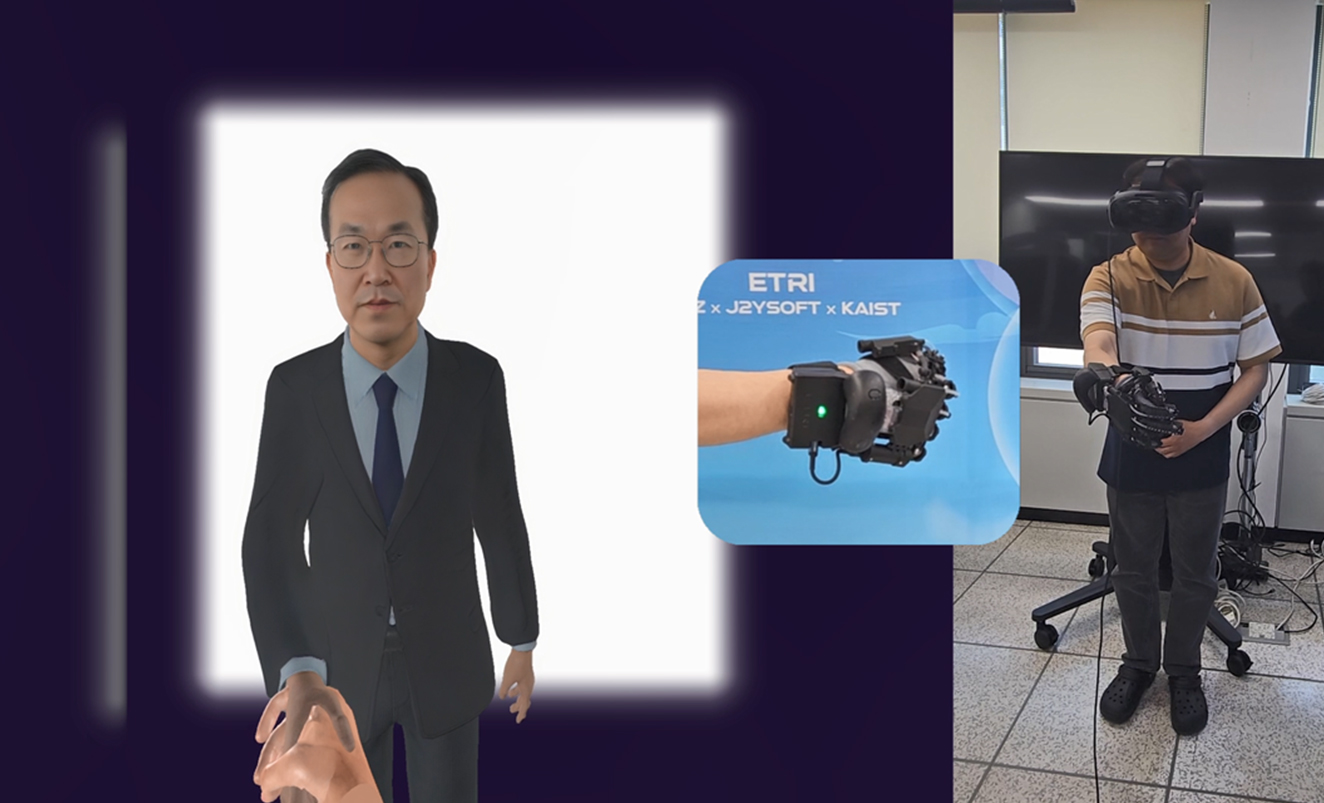 Eye contact, virtual handshake demo content with real-time stereoscopic realism technology
Eye contact, virtual handshake demo content with real-time stereoscopic realism technology
Second, the real-time stereoscopic realism technology for digital humans utilizes generative artificial intelligence (AI) in a head-mounted display (HMD) environment based on binocular imaging to enhance the three-dimensionality and natural facial expressions of digital humans in real time. Traditionally, high-quality digital humans require large system resources to be realized in real time, but with this technology, even relatively low-quality video sources can be enhanced to appear realistic and lifelike. This technology enables natural, lifelike facial expressions even in remote conferencing environments.
This demonstration system used a head-mounted display (HMD) and sensors to naturally reflect a variety of non-verbal cues from the user’s hands, feet, gaze, facial expressions, mouth shape, voice, and more on the digital avatar. In particular, ‘3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)4)’, an AI-powered 3D background generation technology, was also applied to create a more realistic sense of space and immersion.
Through this system, visitors experienced making eye contact and shaking hands with remote participants via avatars, just as if they were in an actual meeting room, vividly immersing themselves in a new dimension of collaboration that goes beyond traditional video conferencing.
Research on the exoskeleton-based active virtual handshake technology is being conducted jointly with the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Neofect Co., Ltd., and the University of Southampton in the UK as part of a research grant project supported by ETRI. The real-time stereoscopic realism technology for digital humans was carried out through the project titled ‘Development of photorealistic digital human creation and 30fps realistic rendering technology’ which is part of the ‘Realistic Content Core Technology Development Project’ funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP).
Dr. Jung Sung Uk, principal researcher of ETRI’s Content Convergence Research Section, said, “This technology will be an important step in shifting the concept of remote collaboration beyond simple video calls to the era of ‘realistic interaction.’ We will continue to develop it into a future collaboration solution that people can directly experience in various fields such as education, industry, and healthcare.”
ETRI will continue to improve the quality and immersion of remote collaboration by integrating cutting-edge technologies in various fields such as XR, AI, haptics, and immersive media. ETRI introduced this technology to the public at ETRI Conference 2025 held in early last month.
4) 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS): The latest video compositing technology to reconstruct realistic three-dimensional scenes from ordinary photos
Dr. Jung Sung Uk, Principal Researcher
Content Convergence Research Section
(+82-42-860-3849, brcastle@etri.re.kr)