ETRI Innovates Water Network Management with Digital Technology
Vol.82 April
- Developing a Digital Twin-Based Water Network Monitoring and Management System to enhance operation and maintenance efficiency
- Performing verification in Daegu and expanding to metropolitan municipalities nationwide to advance the technology
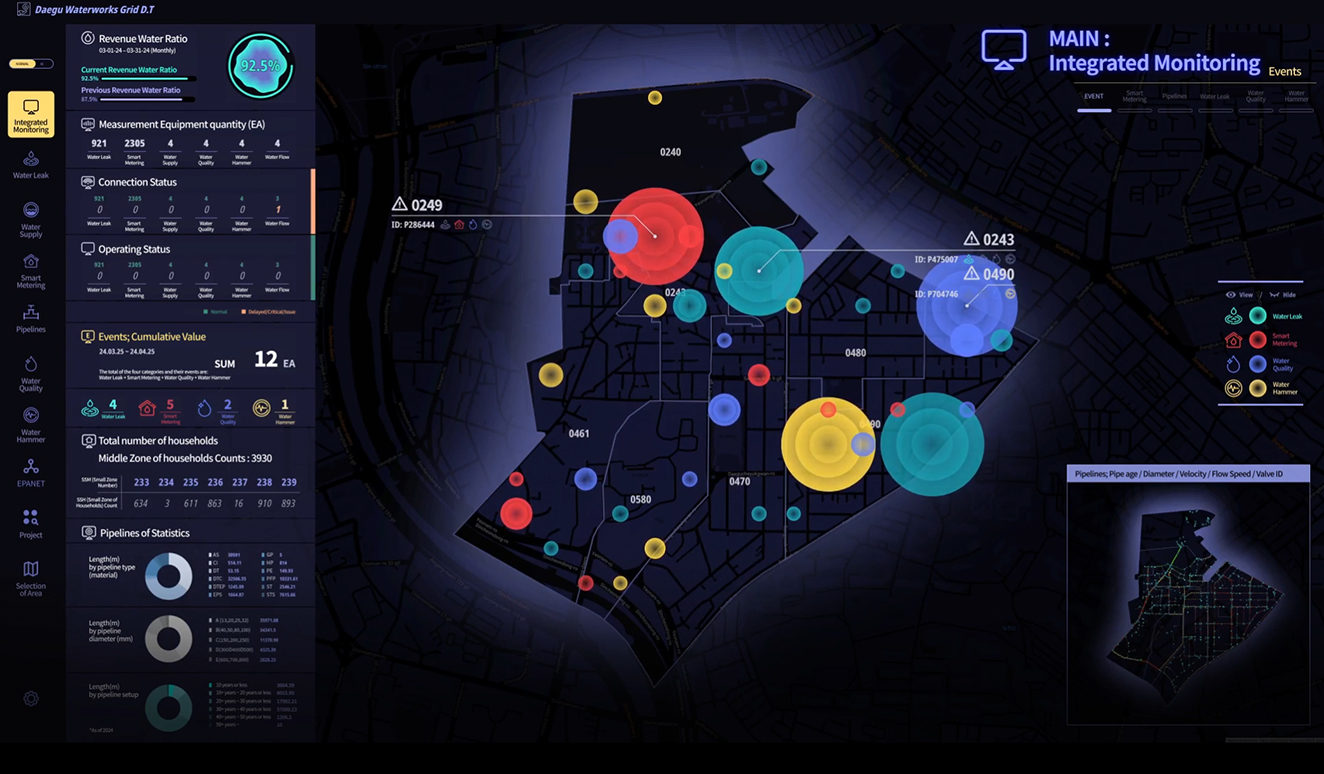 Main Screen of the Digital Twin-Based Water Network Monitoring System
Main Screen of the Digital Twin-Based Water Network Monitoring System
Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a technology that can lead technological innovation in the field of water supply network management. It is expected to play a major role in increasing the efficiency of water supply management in the future.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that it has developed a ‘Digital Twin1)-Based Water Network Monitoring and Management System’ that can collect and comprehensively analyze various data to detect abnormal situations that may occur in the water supply network, and simulate and predict the operational status of the water supply network.
The researchers expect that if the developed system is deployed in the water supply industry, it will dramatically improve the operation and maintenance efficiency of the water supply network and the stability of tap water supply.
There are two main core technologies in the control system. The first is real-time monitoring technology based on sensor data analysis. This technology can perform ▲indoor and outdoor leak detection of water supply networks ▲identification of suspected leakage areas ▲detection of water quality abnormalities ▲water impact recognition and location estimation.
The second is simulation and prediction technology, which can conduct △simulation of flow, pressure, and residual chlorine in the water supply network △simulation of water quality accidents △recommendation of control valves to isolate leaky pipes △evaluation of pipe age △prediction of weekly water demand.
1) Digital twin: It refers to the implementation of real-world facilities or processes in virtual reality as software (model), and the model is mainly implemented by combining physical models and data-based models.
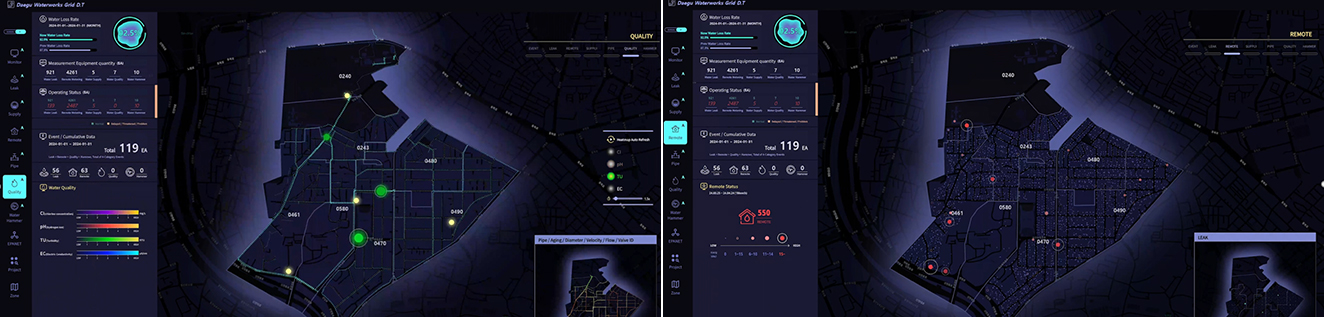 What a water quality telemetry screen looks like
What a water quality telemetry screen looks like
The existing water network management system manages various data required for monitoring, simulation, and prediction in a decentralized manner, including geospatial information, environmental data, pipeline properties, pressure, flow, water quality, vibration, and smart metering data.
However, this Digital Twin-Based Water Network Monitoring and Management System developed by ETRI can consolidate them and view them at a glance. The data-driven AI models implemented in this system are designed to be sensitive to anomalies that may occur due to communication errors or sensor malfunctions. It is also periodically updated to reflect the latest data characteristics.
The system is equipped with various water leakage management technologies such as ▲outdoor pipe leakage detection technology based on vibration data analysis ▲control valve recommendation technology for isolating leaky pipes ▲indoor water leakage estimation technology based on smart metering2) data analysis ▲suspected water leakage area identification technology, etc.
2) Smart Meter: A digital water meter that measures tap water usage in real time and transmits data remotely for integrated monitoring and analysis
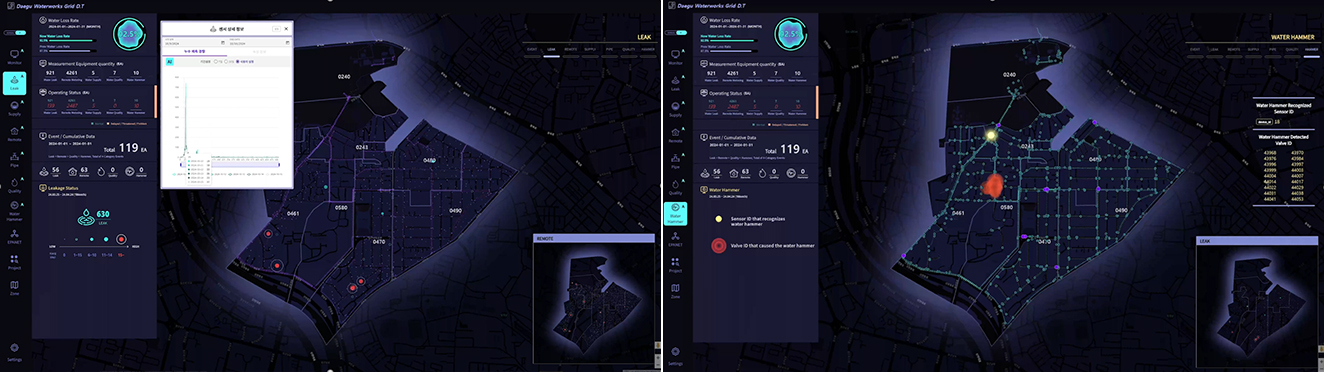 What a leak or water impact looks like
What a leak or water impact looks like
The developed system is capable of integrating and monitoring multiple abnormalities such as water leakage, water quality abnormalities, water impact, etc. This can improve the accuracy of detecting correlated anomalies.
The simulation function installed in the system by the researchers intuitively visualizes the distribution of flow, pressure, and residual chlorine values. This feature helps administrators select locations for new meter installations or identify areas where water flow is stagnant.
They have also developed a function to simulate how flows and pressures will change when large-scale capacity is added to an area. It is now possible to simulate how the residual chlorine value changes when some of the tap water inside the pipe is discharged to the outside.
The researchers explained that they implemented new functions based on EPANET that could not be provided in the existing US EPANET (Environmental Protection Agency Network)3) simulator. These additional features enable the simulation of various situations in the water supply network, providing administrators with the practical and useful information needed to effectively operate and maintain the water supply network.
Currently, the field demonstration of the developed system is being successfully conducted in one central district under the jurisdiction of the Office of Waterworks, Daegu Metropolitan City. They are in the process of upgrading the system to increase its field applicability, scalability, and reliability.
Last year, ETRI researchers participated in ‘2024 Water Korea’, the largest specialized water industry exhibition in Korea, and ‘ACE24’, a global water industry exhibition in the U.S., and received great response from related experts. They also participated in ‘FIX 2024’ and ‘Korea International Water Week 2024’, which were held at Daegu EXCO, and received a lot of attention.
This Digital Twin-Based Water Network Monitoring and Management System can enhance the reliability of water services by maximizing the safety and efficiency of the water supply network through real-time integrated monitoring of the condition of the water pipeline network and improving the quality of tap water. It can also comprehensively simulate and predict the behavior of water supply networks to support accurate decision-making and reduce unnecessary operational and maintenance costs.
“We will provide active support such as testbeds and data sharing so that the integrated water network management system being developed by Daegu Water Cluster resident companies can be practical and advanced in the field, not in virtual reality,” said Baek Dong Hyun, head of the Office of Waterworks, Daegu Metropolitan City.
Byun Woo Jin, vice president of ETRI’s Daegu Gyeongbuk Research Division, said, “The system is equipped with digital core technologies such as leak detection in the water supply network. In the future, we plan to upgrade the developed system and contribute to raising the domestic water supply network management technology to the world’s highest level.”
Based on this achievement, the research team plans to expand the demonstration area to local governments across the country and advance the technology. This achievement is the result of the DGIST General Project supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
3) EPANET: Developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), it is open source software for water network analysis and is widely used in water supply-related academia and industry. It can simulate changes in water flow, pressure, and residual chlorine in a water network.
Kim Kwangju, Director
AI Infrastructure Research Section
(+82-53-670-8039, kwangju@etri.re.kr)