Wherever you may be, you can easily access the data and videos on overseas websites, such as YouTube and Facebook. How is it possible that we can watch a video uploaded in the US within just one second? You may think it’s because of the advanced wireless technology, but the world is in fact connected with wires. Of course, we can enjoy fast wireless internet service, thanks to the development of wireless communication devices. However, wireless communication is limited by distance. For example, as you move away from a wireless internet router placed in a house or school, the communication speed becomes slow, and eventually the connection is cut off.
Since the same applies to the internet service provided by mobile communication companies, you cannot enjoy the wireless internet service if you are deep inside a forest or on a lonely island in the ocean. Then, how is it possible that we enjoy the communication through the internet in all parts of the world? It’s because the countries are connected with each other through submarine cables.
01
Data Coming Over the Ocean
This might give rise to a question. For example, if you click in Seoul a video that was uploaded in New York, the time required for loading is just one second. Does it mean that the data travel from New York to Seoul within just one second? The answer is No. The data do not travel hundreds of thousands of kilometers to come to you after you click the video. It is highly probable that the data of the video have already been saved in data centers near to you. It’s true that the data travel in the path of ‘submarine cable → data center → users’, but the data that you frequently use actually come from data centers close to you and are delivered to your devices.
However, these data centers also have troubles due to the development of technologies as well as the explosive increase of data traffic. So, as the data centers are used more and more, the network itself should be advanced more and more. Is it because the data centers are too small? No. Each state of the US has a data center that is three times as large as the Jamsil Olympic Stadium.
02
Essential Technology for Speed
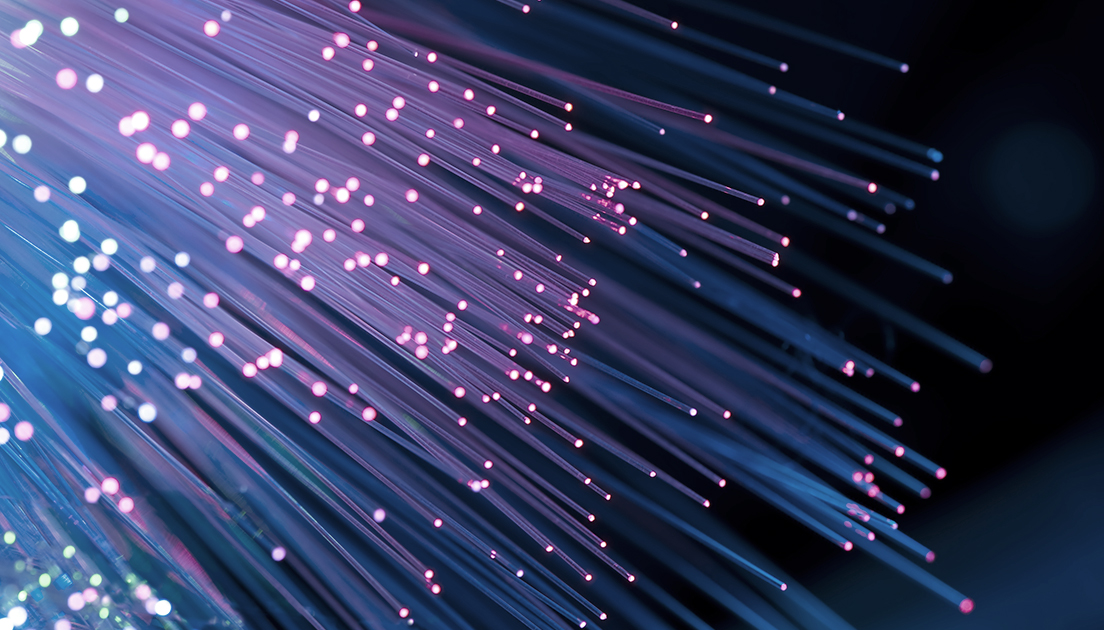

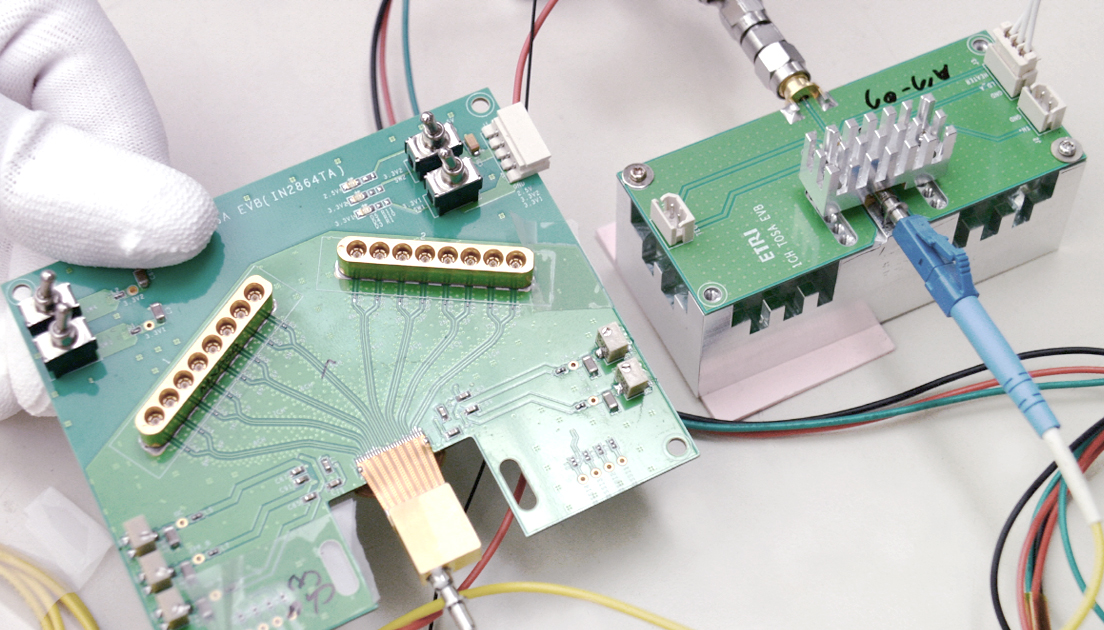
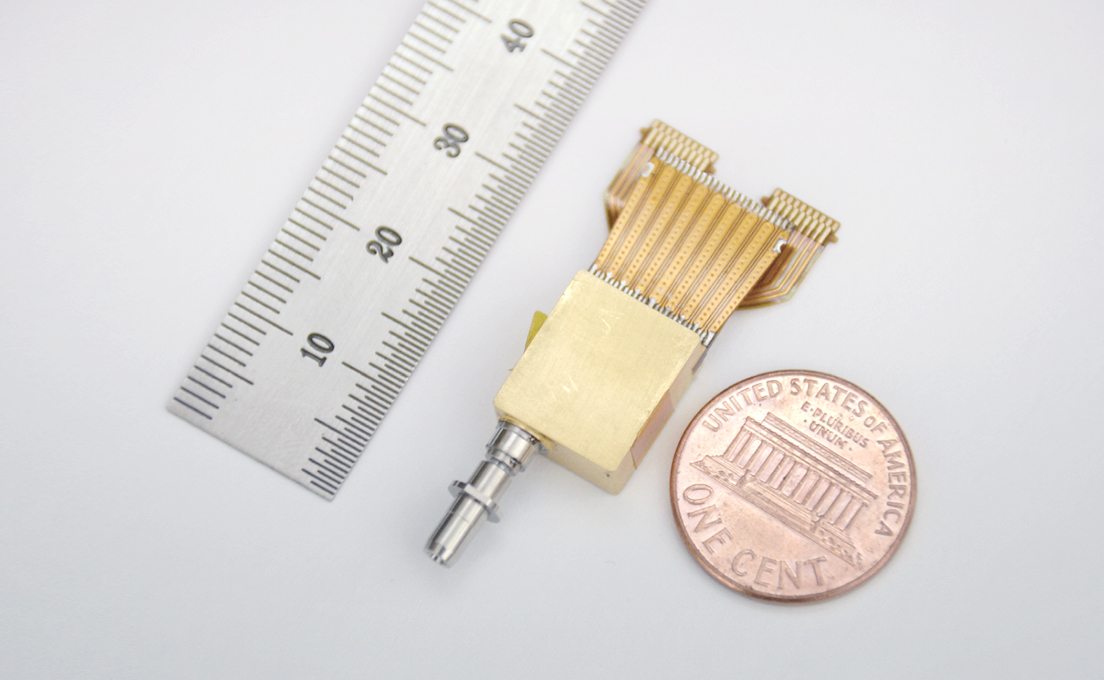
Management of the data centers for efficiently saving information and connecting users is important, but the connection speed is critical. Optical fiber is at the core of the technology, as it serves as a ‘highway’ for fast data transmission. Optical fibers are also included in the submarine cables deep in the oceans. Optical fibers transmit communication signals by means of light. A submarine cable, consisting of a bunch of optical fibers, is wrapped by copper, polycarbonate, aluminum, and metal wires to prevent breaking or corrosion.
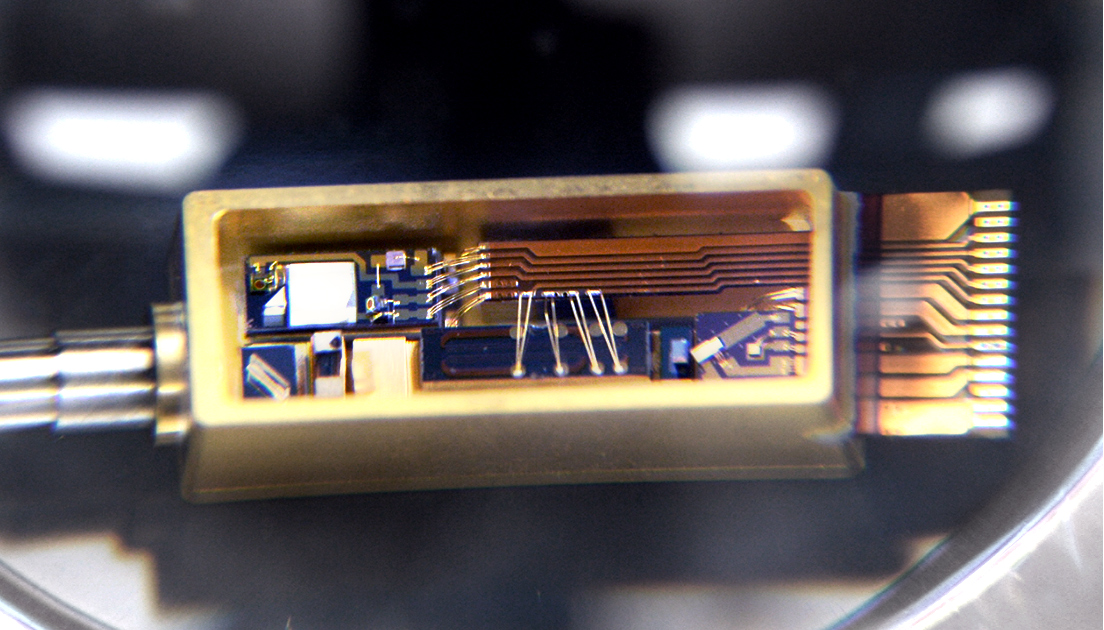
Korea has relied on the import of the parts for the conventional optical transmission and reception system. However, they were recently localized in Korea by ETRI’s Optical Network Research Group. This group has developed a technology that allows communication in traffic over four times as high as now without additional installation of optical cables.